Article in brief
Reflex reflex pain syndrome of the foot is a complex regional pain syndrome requiring appropriate management.
- Pathological mechanism: dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system following trauma, even minor, causing an intense inflammatory cascade.
- This condition progresses in three distinct phases: inflammatory (1-3 months), dystrophic (3-6 months), and atrophic (after 6 months).
- Diagnosis is based on clinical examination, the Budapest criteria, and imaging studies showing characteristic bone demineralization.
- Treatment combines medications analgesics, appropriate physiotherapy, and sometimes neurostimulation for resistant cases.
Foot reflex pain syndrome is a painful condition that can significantly affect the quality of life of those affected. This complex regional pain syndrome is characterized by intense pain, often disproportionate to the triggering event. Understanding its mechanisms, identifying its symptoms, and knowing the available treatments is essential to better manage this debilitating condition.
Understanding Foot Reflex Syndrome: Causes and Mechanisms
Reflex pain syndrome, also known as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), particularly affects the foot due to its anatomical complexity and vulnerability to trauma. This condition generally develops following a traumatic event, even minor in some cases.
The main causes of foot reflex pain syndrome include various triggering factors. Trauma such as sprains, fractures, or surgical procedures are the most common causes. In some cases, a simple contusion can trigger this pathological process. Other factors may also be involved, such as nerve damage, vascular disorders, or certain pathologies such as stroke.
Physiologically, CRPS results from a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. This disruption triggers a cascade of inflammatory and neurovegetative reactions in the affected area. Disruption of pain regulation mechanisms explains the intensity of the symptoms experienced, sometimes similar to tingling in the foot but generally much more intense.
The progression of CRPS is classically divided into three phases:
- Hot or inflammatory phase (1 to 3 months): characterized by intense pain, edema, and localized heat
- Dystrophic phase (3 to 6 months): with persistent pain, progressive cooling, and joint stiffness
- Atrophic phase (beyond 6 months): marked by chronic pain and sequelae Functional
It is interesting to note that CRPS can also affect other parts of the body, but the foot remains particularly vulnerable due to its support function and its rich supply of nerve endings. This condition can affect anyone, but appears to be more common in women between the ages of 40 and 60.

Symptoms and Diagnosis of Reflex Foot Syndrome
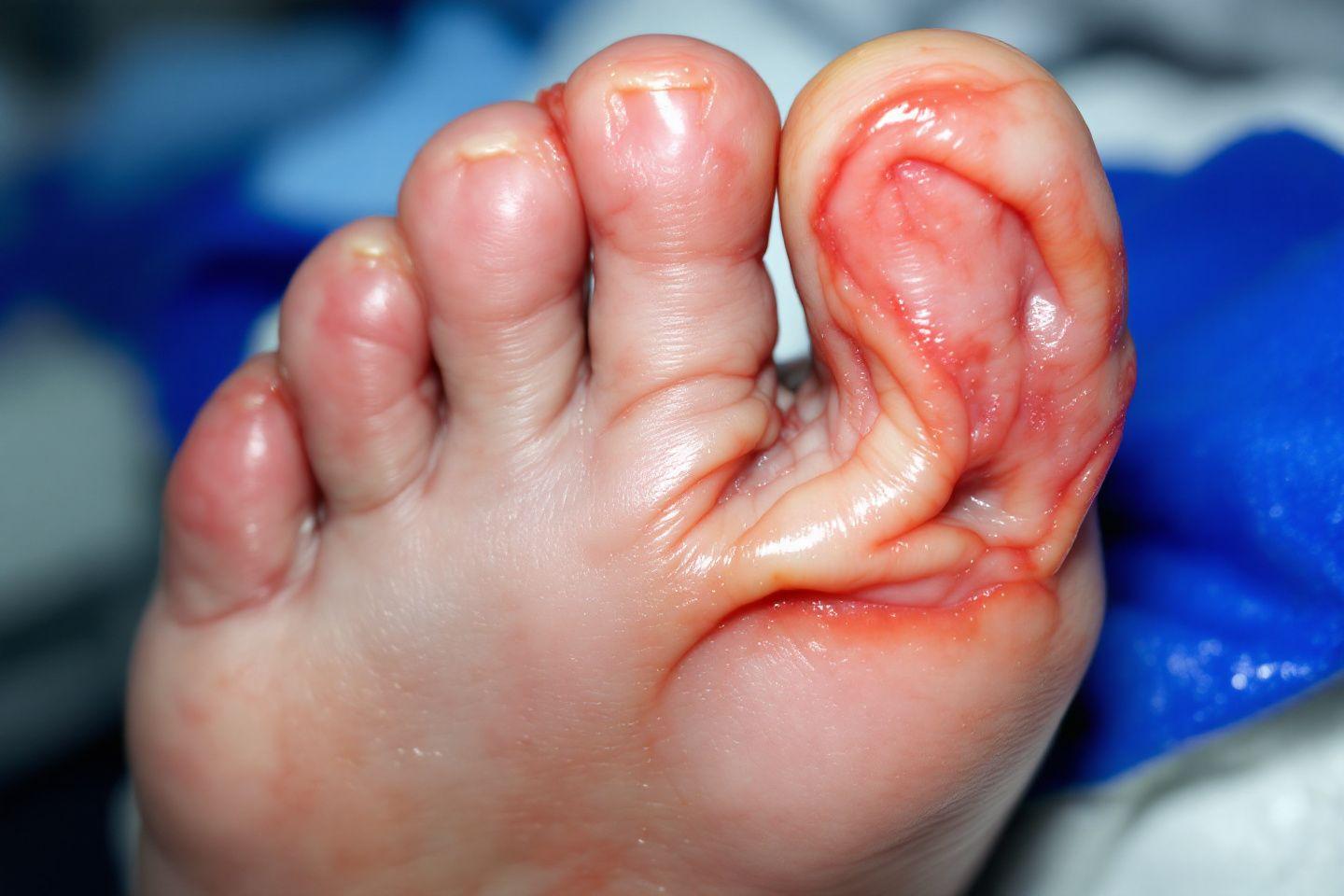
Recognizing the symptoms of reflex foot syndrome is the first step toward appropriate treatment. Pain is the primary symptom of this condition. It is characterized by its intensity, which is often disproportionate to the initial event, and by its persistence despite conventional treatments.
The clinical manifestations of CRPS of the foot vary depending on the stage of development but generally include:
Intense and persistent pain, often described as burning or stabbing. This pain may resemble pain under the soles of the feet but generally extends to the entire foot. Vasomotor disturbances such as swelling (edema), localized heat, and then progressive cooling. Changes in the skin which become shiny, thin and have sweating problems. Progressive joint stiffness can lead to significant functional limitations.
Diagnosis is based primarily on clinical examination, but various additional tests can help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other pathologies:
| Examination | Typical findings in CRPS |
|---|---|
| Plain X-ray | Bone demineralization in patches (after several weeks) |
| Bone scan | Early tracer uptake |
| MRI | Bone marrow edema and soft tissue abnormalities |
| Laboratory tests | Normal (allows exclusion of other pathologies) |
The physician will also rely on the Budapest diagnostic criteria, established specifically for complex regional pain syndrome. These criteria take into account the symptoms reported by the patient and the objective signs observed during the clinical examination.
It is essential to seek prompt medical attention in the event of tingling in the foot associated with intense and persistent pain, particularly after trauma, even minor. Early diagnosis significantly improves the prognosis of CRPS.
Therapeutic Strategies to Relieve CRPS of the Foot
Management of CRPS of the foot requires a multidisciplinary approach. The earlier treatment is initiated, the better the chances of full functional recovery.
The drug treatment of CRPS relies on several classes of medications:
- Conventional analgesics and anti-inflammatories to relieve the initial pain
- Tricyclic antidepressants and antiepileptics (pregabalin, gabapentin) to treat the neuropathic component
- Calcitonin and bisphosphonates to slow bone demineralization
- Corticosteroid therapy sometimes used during the acute inflammatory phase
Physiotherapy is a fundamental pillar of treatment. It helps maintain joint mobility, prevent stiffness, and gradually restore normal function. Rehabilitation must be adapted to the intensity of the pain to avoid any exacerbation of symptoms.
Other therapeutic approaches can complement treatment:
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) uses electrical impulses to modulate pain perception. Sympathetic blocks aim to temporarily interrupt the nerve pathway responsible for maintaining pain. effective techniques for rapid foot pain relief such as cryotherapy or certain orthotics can provide additional relief.
In cases resistant to conventional treatments, implantable spinal cord stimulation may be considered. This advanced technique blocks the transmission of pain signals to the brain using electrodes placed near the spinal cord.
The prognosis for CRPS is generally favorable with early and appropriate treatment. The majority of patients recover within 6 to 24 months, although some may suffer from functional impairment or residual pain. Psychological support also plays an important role in managing this chronic and painful condition.



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.